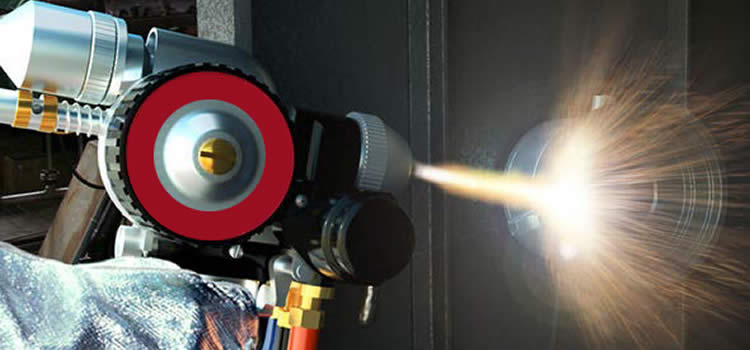
A Flame Spray Gun is a tool that uses heat to spray melted material onto things. It makes coatings on surfaces to protect and make them stronger. Here is how it works: Fuel gas or oxygen is burned to make a flame. This flame heats the material until it melts. High speed air or gas then spray the melted material onto the surface you want to coat. This sticks the coating on tight. A Thermal Spray Gun comes in different kinds. Each kind is good for certain jobs. The kinds are wire arc spray, powder flame spray, and twin wire arc spray. They all make tough coatings but in different ways. Flame Spray Guns have many uses. They help stop rust and make surfaces better. Industries like aerospace, cars, and manufacturing use them to make coatings that last a long time.
Metalizing Spray Gun use powder feeders to help coat things evenly. Powder feeders control how the melted material comes out so it can be put on accurately and in a controlled way. Safety is very important when using Flame Spray Guns. You must follow rules, have good airflow, and wear protective clothes. Like all machines, Flame Spray Guns can sometimes have problems. The coating may not be smooth or the nozzle may get blocked. But there are ways to fix these issues and make the machine work well again. It is important to clean the equipment and take good care of it regularly. This helps the machine last a long time and keep giving the same good results.
Types of Flame Spray Gun

There are different kinds of flame spray guns. Each kind is made for special jobs and factory needs. Here is a quick look at the main types of flame spray guns:
- Wire Arc Spray Guns: This type of flame spray gun uses electricity to melt metal wire. Small drops of melted wire are shot at the surface being coated. Anarc spray gun is often used to protect against rust, fix worn parts, and make heat shield coatings.
- Powder Spray Guns: These guns burn gas and oxygen to melt powder materials. The melted powder is then sprayed on the surface. Combustion powder spray guns are good for making thick coatings from things like metals, ceramics, and plastics.
- Twin Wire Arc Spray Guns: Twin Wire Arc Spray Guns are like wire arc spray guns but have two wires. The two wires make the coating better and look more even. They are good when the coating needs to stick well and be the same all over.
- High-Velocity Oxygen Fuel (HVOF) Spray Guns: High-Velocity Oxygen Fuel (HVOF) Spray Guns use a mix of fuel and oxygen that catches fire. HVOF Gun makes a very fast flame to melt and spray materials. Coatings from these guns are very tight and smooth with little holes. They also sticks to things well.
- Detonation Spray Guns: Detonation Spray Guns make coatings by lighting fuel and oxygen in a closed space. This makes a jet of particles that goes very fast. They use these to put on wear-resistant coatings on different materials.
- Plasma Spray Guns: Plasma guns utilize a high-temperature plasma arc to melt and propel materials onto the substrate. Plasma HVOF Spray Gun is commonly employed for high-performance coatings in aerospace, automotive, and medical industries.
- Flame Wire Spray Guns: These guns use an oxy-acetylene flame to melt a consumable wire, creating coatings with controlled thickness. Suitable for applications where precise control over coating thickness is crucial.
Working of Flame Spray Gun
Using Flame Spray Guns needs careful steps to coat things well with heat. Here is a basic look at how Flame Spray Guns work:
- Fuel and Air Mix: First, a mix of fuel and air goes into the Flame Spray Gun. Common fuels are acetylene, propane, or hydrogen. It depends on what you use it for.
- Start the Fire and Burn: The fuel and air mix lights on fire inside the gun. It makes a very hot flame. The controlled fire makes heat for spraying things with heat.
- Material Melting: Heat from burning things is used to melt a material like wire or powder in some flame spray guns. The strong heat melts the material and turns it into a liquid.
- Propulsion of Molten Material: At the same time, air or gas is pushed really fast into the gun. This air stream picks up the liquid material and throws it hard at the substrate.
- Coating Creation: When the melted material touches the base, it hardens. The speed of the sprayed material, while it is melted, makes it stick well and spread evenly on the base.
- Control Mechanisms: Flame Spray Guns have controls to manage things like fuel, oxygen, and how fast the carrier gas moves. These controls help make coatings just right and under control.
- Types of Flame Spray Techniques: Flame Spray Guns come in different types. They work in similar ways but each type is made for different jobs. Wire arc spray guns, powder spray guns, and other types of each have their special ways of doing the coating.
- Cooling and Solidification: The part being coated, usually metal, takes the heat from the sprayed material very fast. This fast cooling and hardening make a tough coating that sticks well to the part.
Flame Spray Guns work by using controlled burning to melt and push materials onto another surface. This makes protective and useful coatings. The Flame Spray Gun can be carefully controlled. There are different kinds that can be used in many ways. This spraying method uses heat so it can help in many industries.
Applications of Flame Spray Gun
Flame Spray Guns are used in many different ways at workplaces, offering helpful coatings and surface changes. Here are some important ways Flame Spray Guns are used:
- Corrosion Protection: Twin Wire Arc Spray Gun is used a lot to put coatings on metal surfaces. These coatings work like a shield. They stops rust and makes parts last longer.
- Aerospace Industry: Flame Spray Guns are used in aerospace to create coatings on engine parts. These coatings make things stronger against heat, protect against wear, and help engines work better.
- Automotive Coatings: Flame spray is used in cars to put coatings on engine parts that resist wear. It also reduces friction. Flame spray is also used to put coatings on car parts to stop corrosion.
- Surface Repair and Rebuilding: Flame spraying is a good way to fix worn or damaged surfaces. Zinc Spray Gun lets you put protective coatings on things to bring them back to their original size and how they work.
- Oil and Gas Industry: In the work with oil and gas, Flame Spray Guns are used to put coatings on parts used in hard conditions outside. This includes putting coatings on pipes, valves, and drilling machines to make them stronger against rust.
- Electronics and Semiconductors: Flame spray technology is applied in electronics and semiconductor manufacturing to create coatings with specific electrical properties. This includes coatings for circuit boards and electronic components.
- Textile Industry: Powder Flame Spray Gun is used in the textile sector to coat machine parts, improving their resistance to wear. This bolsters the durability and effectiveness of textile production machinery.
- Medical Devices: The medical sphere also uses flame spray coatings, especially for making surfaces of implants compatible with the body. Such coatings aid in better adaptability with human tissues, thus cutting down the chances of rejection.
- Power Generation: Elements in power stations, such as turbine blades and boiler tubes, gain from the applications of Flame Spray Guns. The coatings provide superior resistance to intense heat, wear, and rust in demanding energy production conditions.
Flame Spray Guns are widely popular in sectors where increased durability, superficial enhancements, and protective layers are vital. The evolving applications of such tools are fostering advancements in the realm of coating technologies and surface modification.
Types of Wires Used in Flame Spray Guns
When it comes to Flame Spray Guns, selecting the right types of wires is essential to attain the desired coating characteristics and performance. Various types of wires serve multiple purposes. Here’s a look at some general types of wires used in Flame Spray Guns:
- Metalizing Wire: Metals such as aluminum, zinc, copper, and stainless steel are applied as fusible wires. These wires liquify under the heat provided by the Flame Spray Gun, generating molten droplets suitable for coating purposes. They’re often employed for rust-prevention coatings, refurbishing weathered components, and offering thermal safeguards.
- Aluminum Wire: Primarily, aluminum wires take the spotlight in Flame Spray uses because they’re light as a feather and fight off corrosion when used as coatings. They’re a popular choice in the aerospace sector for generating thermal boundary layers, as well as in many industries where the battle against rust is real.
- Zinc Wire: Zinc wires are favorites for their knack to resist corrosion. When these are sprayed onto a base material, they construct a protective shield of zinc that serves as a selfless barrier, inviting rust first on itself. You’ll find these perfect where guarding against rust is the main gig, like in sea-based scenarios.
- Copper Wires: For their prowess in electricity conduction and standing up to corrosion, copper wires are the go-to choice. When the need is for superior electrical traits, these wires come in handy. In the realm of electronics and semiconductor firms, these are employed to coat parts needing specific electrical attributes.
- Stainless Steel Wires: Stainless steel wires don’t get damaged by water and chemicals. They have tough coatings that can deal with bad places. Cars, oil, and gas, and factories use them a lot for coatings that don’t wear away or rust.
- Nickel-Based Alloy Wires: Nickel-based alloy wires, such as Inconel, offer high-temperature resistance and excellent corrosion properties. These wires are suitable for extreme environments. Commonly used in aerospace, power generation, and chemical processing industries for coatings exposed to high temperatures and corrosive conditions.
- Molybdenum Wires: Molybdenum wires are good because they can be hot without melting. They conduct heat well and don’t break down from chemicals. They stay strong even in very hot places. People use them a lot when things need to work well in high heat, like protecting airplane and spaceship parts or in making electronics and factory machines.
- Composite Wires: Composite wires are made with different materials together, often a metal frame with ceramic or other extras added. These wires give better coating options. They are used for special jobs where special qualities are needed, like being harder or resisting heat better.
It is very important to choose the right kind of wire for Flame Spray jobs. This will help get the coating you want for protection from rust, wear, or certain electrical needs. There are many wire options so you can pick one that works best for your needs. This helps flames spraying meet what different businesses require.
Types of Coating Powder Used in Flame Spray Guns
Different coating powders are used in Flame Spray Guns to give coatings special traits. Here are some usual coating powders used in Flame Spray Guns:
- Metallic Coating Powders: Metallic powders are made from metals like aluminum, zinc, copper, and mixes. When these powders touch the heat from the Flame Throw Gun, they melt and make protecting covers. They are commonly used to stop rust, fix worn-out parts, and give heat protection in many industries.
- Tungsten Carbide Coating Powder: Tungsten Carbide powder is a hard and wear-resistant material, often combined with a metal matrix. It provides coatings with exceptional hardness, toughness, and resistance to wear. Widely used in applications requiring extreme wear resistance, such as in the production of cutting tools, industrial machinery components, and wear-resistant coatings for various surfaces.
- Aluminum Coating Powder: Aluminum powder is a good choice because it is light and does not rust easily. It makes coatings that stop corrosion and give heat protection. People use it a lot in aerospace for heat barrier coatings and in normal industries to stop corrosion.
- Zinc Coating Powder: Zinc powder is known for its anti-corrosive properties. When melted by the Flame Spray Gun, it creates a protective zinc layer on the substrate, acting as a sacrificial barrier against corrosion. Ideal for applications where corrosion protection is paramount, such as marine environments.
- Ceramic Coating Powders: Ceramic powder includes materials like alumina, zirconia, and chromium oxide. These powders provide coatings with enhanced hardness, wear resistance, and high-temperature stability. Used in applications where durability, abrasion resistance, and thermal stability are crucial, such as in the automotive and aerospace industries.
- Polymer Coating Powders: Polymer powders, often in powder form with specific additives, are used for specialized applications. These coatings offer unique properties such as flexibility, adhesion, and resistance to chemicals. Applied in industries like electronics, where coatings with specific properties, such as electrical insulation or chemical resistance, are required.
- Cermet Coating Powders: Cermet powders are a combination of ceramics and metals, offering a blend of hardness, wear resistance, and toughness. They provide coatings with balanced properties. Commonly used in applications where a combination of hardness and toughness is essential, such as cutting tools and wear-resistant components.
- Nickel-Based Alloy Coating Powders: Nickel-based alloy powders, such as Inconel, exhibit high-temperature resistance and corrosion properties. These powders are suitable for coatings in demanding environments. Widely used in aerospace, power generation, and chemical processing industries for coatings exposed to extreme temperatures and corrosive conditions.
- Molybdenum (Moly) Coating Powder: Molybdenum powder is valued for its high melting point, thermal conductivity, and corrosion resistance. It forms coatings suitable for high-temperature applications. Applied in industries requiring coatings with stability in extreme temperature conditions, such as aerospace and electronics.
The choice of coating powder in Flame Spray applications depends on the desired properties of the resulting coating, ranging from corrosion resistance and thermal insulation to hardness and wear resistance.